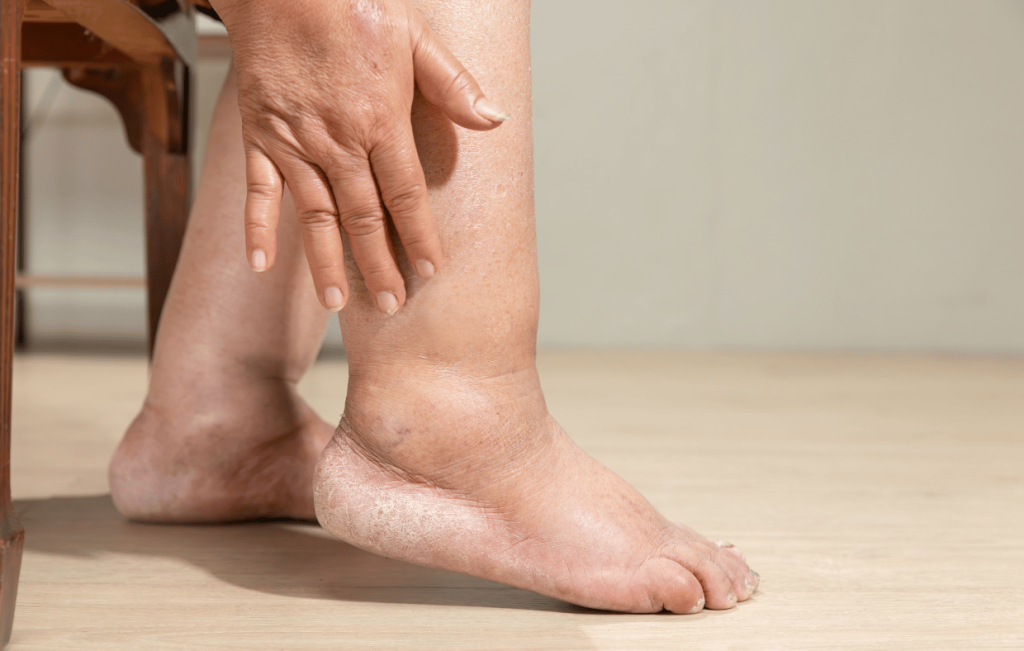
Lipedema is a chronic condition causing abnormal fat accumulation from the ankles to the thighs/hips and upper arms. This adipose disorder primarily affects women and is often misdiagnosed as obesity or lymphedema.
Management involves lifestyle changes, medical therapy, and dietary modification. Diet plays a crucial role in lipedema management, focusing on anti-inflammatory foods, low-carb options, and specific nutrients that improve overall health and mobility.
For scientifically proven ways to manage lipedema, Mitolyn offers insights into the role of mitochondria in controlling chronic diseases, including lipedema.
What is Lipedema and What Are Its Dietary Requirements?

Lipedema often involves chronic inflammation, fluid retention, and insulin resistance. An appropriate diet reduces inflammation, controls weight, and improves lymphatic function.
Overall Dietary Guidelines for Lipedema Sufferers
- Reduce chronic inflammation: Consume anti-inflammatory ingredients to alleviate swelling and pain.
- Enhance lymphatic health: Maintaining adequate hydration and nutrient intake to improve lymphatic function and decrease fluid retention.
- Manage weight: While calorie restriction alone doesn’t burn lipedema fat, a low-carbohydrate diet can be effective for weight management.
- Support adipose tissue health: Consume healthy fats and lean proteins to promote adipose tissue health and function.
Lipedema-Approved Diets
Several dietary approaches have proven successful in managing lipedema symptoms.
1. Ketogenic Diet (Keto Diet)
A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that forces the body to use fat for energy. This diet normalizes blood sugar levels, lowers insulin secretion, and alleviates chronic inflammation.
Benefits for Lipedema:
- Lowers chronic disease risk factors
- Promotes weight loss without drastic calorie restriction
- Assists in controlling insulin resistance
Note: Initial adaptation may cause temporary discomfort.
2. Mediterranean Diet
This diet emphasizes anti-inflammatory foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins.
Staples of the Mediterranean Diet:
- Olive oil: Promotes healthy weight and reduces inflammation
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines): Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, crucial for fighting inflammation
- Leafy greens: High in nutrients that promote lymphatic function
- Whole fruits (e.g., citrus): Source of vitamin C, which can improve blood glucose levels and reduce oxidative stress
3. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods is crucial for lipedema sufferers, as chronic inflammation drives disease progression.
Foods that Fight Inflammation:
- Turmeric and ginger: Strong anti-inflammatory benefits
- Berries: Rich in antioxidants
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, Brussels sprouts): Aid in detoxification
- Nuts and seeds: Contain healthy fats that promote adipose tissue health
4. Low-Carbohydrate and RAD Diet
The Rare Adipose Disorder (RAD) Diet combines a low-carbohydrate approach with a focus on healthy proteins and fatty acids.
Lipedema Low-Carb Diet:
- Restricts simple sugars in white bread and processed foods
- Promotes whole grains with a low glycemic index
- Encourages lean animal proteins such as poultry and fish
Diet Tips for Lipedema Patients
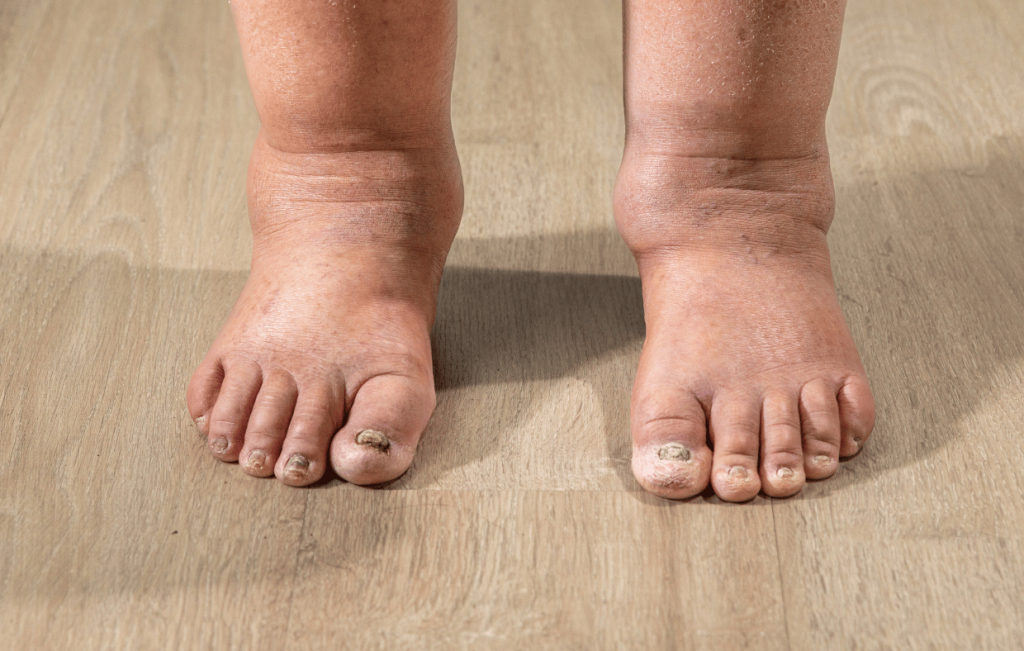
1. Managing Insulin Resistance
Lipedema is often exacerbated by insulin resistance. Reduce high-glycemic foods and adopt a balanced diet.
2. Water Retention and Hydration
- Drink plenty of water to support your lymphatic system
- Limit dairy products if inflammation is present
- Reduce artificial sweeteners that can affect blood sugar levels
3. Essential Nutrients
- Vitamin D: Supports overall health and addresses mobility issues
- Vitamin C: Essential for lymphatic function and fatty tissue health
- Protein: Recommended for muscle maintenance and overall health
Medical and Lifestyle Measures
1. Surgical Treatments
In severe cases, lipedema treatment may involve bariatric surgery or liposuction to remove excess lipedema fat. Consult healthcare professionals for these options.
2. Compression Garments
Wear compression garments to improve circulation and decrease fluid retention in the lower extremities.
3. Regular Physical Activity
Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical exercise, to control weight and body mass index.
Conclusion
A carefully structured diet is vital in managing lipedema. The best diet incorporates elements from ketogenic, Mediterranean, low-carbohydrate, and anti-inflammatory diets. Healthy nutrition, reduced carbohydrate intake, and essential nutrients can significantly improve the quality of life for lipedema patients.
To learn more about mitochondrial health and its relation to lipedema treatment, visit Mitolyn, a hub of scientific and health innovation.
Q&A: On the Best Diet for Lipedema
Q: Is there a special diet for lipedema?
A: Yes, a lipedema diet focuses on reducing inflammation, managing weight, and supporting lymphatic function. A low-carbohydrate, anti-inflammatory approach can benefit many patients by reducing fluid retention and fat accumulation in the lower body.
A high-fat diet, such as the ketogenic diet, shows promising results by stimulating fat metabolism instead of storage.
Key dietary principles include:
- Increasing intake of fresh fruits, especially citrus, for their anti-inflammatory effects
- Eliminating processed foods and sugars that contribute to weight gain
- Prioritizing whole foods to improve general health and alleviate lipedema symptoms
Q: What antioxidants are good for lipedema?

A: Antioxidants help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, crucial in managing lipedema. Beneficial antioxidants include:
- Vitamin C (found in citrus fruits): Aids collagen production and supports lymphatic health
- Vitamin E (in nuts and seeds): Promotes skin elasticity and tissue health
- Polyphenols (in green tea, berries): Reduce inflammation and enhance overall health
- Quercetin (in onions and apples): Supports weight control and has anti-inflammatory properties
Incorporating these antioxidants into your daily diet can significantly improve lipedema symptoms over time.
Q: How to heal lipedema naturally?
- Dietary Changes: Adopt a targeted diet that limits weight gain and secondary lymphedema risk. A low-carbohydrate and anti-inflammatory approach may be beneficial.
- Regular Movement & Lymphatic Support: Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming or rebounding to stimulate the lymphatic system and reduce fluid retention.
- Compression Therapy: Wear compression garments to support lymphatic function and reduce swelling in the upper body and lower legs.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to aid detoxification and prevent water retention.
- Holistic Approaches: Consider lymphatic massage, dry brushing, and acupuncture, which have benefited some lipedema patients.
Q: What supplements are good for lipedema?
A: Targeted supplements can support metabolic health and lymphatic function in lipedema patients:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Reduce inflammation and improve blood circulation
- Magnesium: Assists with fluid balance and muscle function
- Vitamin D: Important for immune function and fat metabolism
- Horse Chestnut Extract: Promotes blood vessel health and may aid weight loss
- Grape Seed Extract: Improves blood flow and reduces swelling
These supplements and appropriate dietary changes can significantly improve general health and support lipedema management.