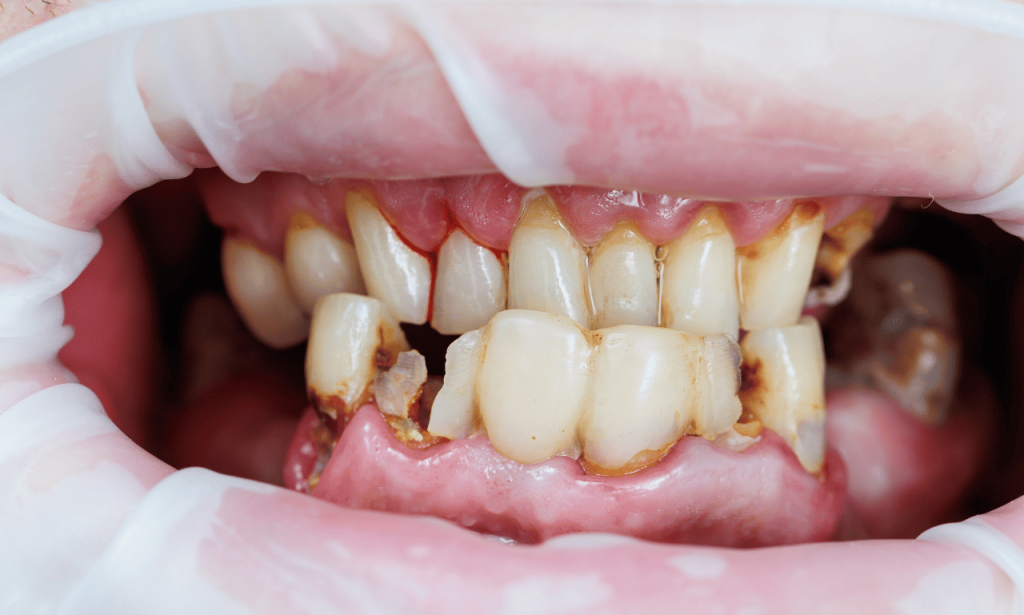
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is one of the leading causes of loose teeth and eventual tooth loss. With the prevalence of this oral health condition, it is crucial to understand how to prevent and treat it. This guide will explore how to fix loose teeth caused by gum disease using the best guide available in 2025.
Intro
Gum disease can start subtly, but if left untreated, it can lead to more severe consequences like tooth loss and bone damage. You’re not alone if you’re dealing with loose teeth due to gum disease.
Millions of adults face this issue, and with the right knowledge and tools, it is possible to restore your oral health. To explore the best options available today, click here.
What Causes Loose Teeth?
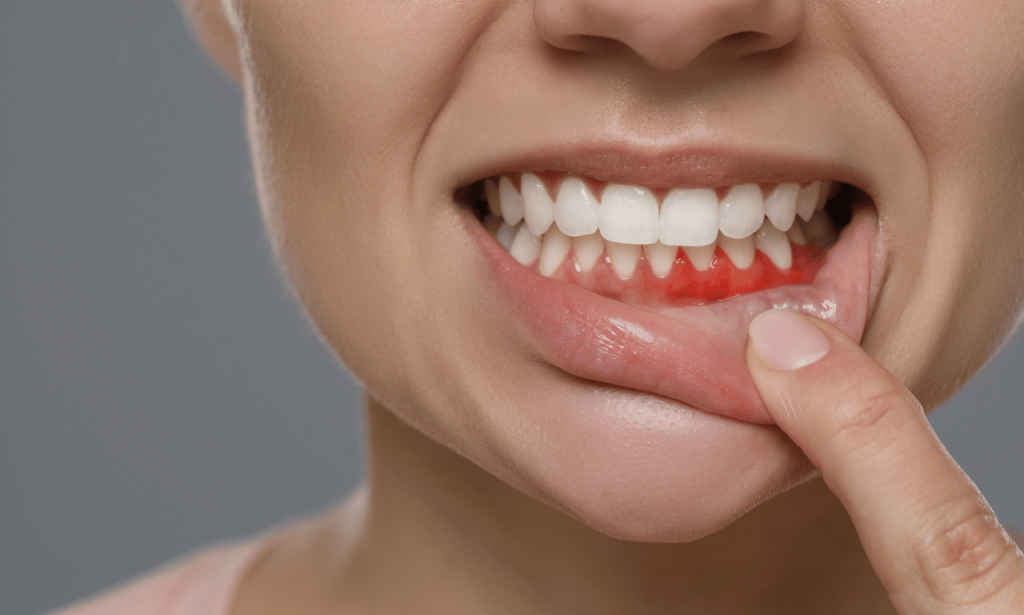

A loose tooth can be caused by several factors, but the most common culprit is periodontal disease. This infection of the gums leads to inflammation, weakening of the bone structure, and the eventual loosening of the teeth. Other causes may include trauma to the mouth, poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, or even a car accident.
Early Signs of Gum Disease
Detecting gum disease in its early stages is critical for preventing further damage. Here are some symptoms to watch for:
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Bleeding gums
- Swollen or inflamed gums
- Receding gum line
- Formation of pockets between teeth and gums
- Wobbly tooth
- Discomfort or pain in the affected area
Understanding Gum Disease and Tooth Loss
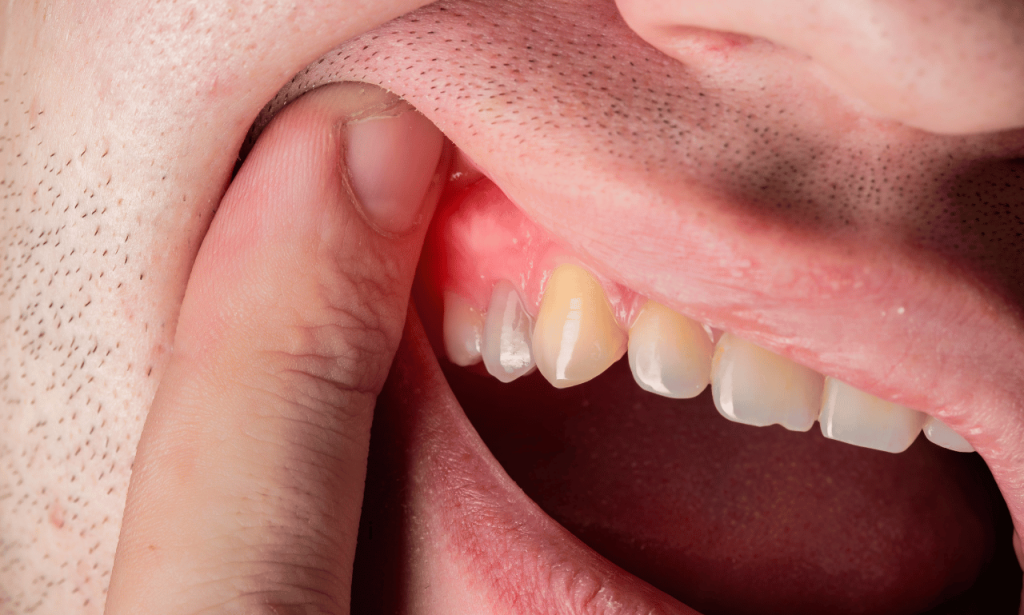
Gum disease can occur in stages, from mild gingivitis (early stage) to advanced periodontitis (severe case). Without intervention, gum disease can lead to the deterioration of the bone and soft tissue, eventually causing tooth loss. This process often starts with dental plaque buildup and progresses if proper care is not taken.
Treatment Options for Loose Teeth Due to Gum Disease
1. Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
The first step in treating loose teeth is often a professional deep cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing. This procedure removes tartar buildup and bacteria from below the gum line, helping to eliminate infection and promote gum healing. Regular dental cleanings are crucial to preventing the recurrence of gum disease.
2. Flap Surgery
In more advanced cases of gum disease, flap surgery may be necessary. During this procedure, the dentist or periodontist lifts the gums to remove bacteria and dental plaque that have accumulated deep within the gum pockets. After the area is cleaned, the gum tissue is sutured back into place to promote healing.
3. Bone Grafts and Soft Tissue Grafts
When bone loss has occurred due to gum disease, bone grafts may be used to regenerate lost bone. This procedure involves taking bone from another part of the body or using synthetic materials to support new bone growth. Similarly, soft tissue grafts can be used to rebuild gum tissue that has receded.
4. Pocket Reduction Surgery
For patients with deep gum pockets that harbor bacteria, pocket reduction surgery is a viable treatment option. This procedure reduces the size of these pockets, making it easier to maintain gum health and preventing the formation of bacterial infections.
5. Dental Appliances
For patients with loose teeth, dental appliances like bite splints can provide stability. A bite adjustment may also be performed to redistribute the forces exerted on the teeth, preventing further damage.
6. Gum Grafts
If the gum line has receded, leading to a loose tooth, a gum graft may be recommended. This involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth and placing it over the affected area to cover exposed tooth roots, which can improve gum health and secure loose teeth.
7. Dental Implants
In cases where tooth loss is inevitable, dental implants offer a permanent solution. Implants replace missing teeth by placing a titanium post into the jawbone, which serves as a sturdy foundation for a crown. This not only restores functionality but also prevents further bone loss.
Preventing Further Damage

Taking proactive steps to prevent further damage to your teeth and gums is essential. Maintaining good oral hygiene habits, including regular brushing and flossing, can help control plaque buildup. Avoiding risk factors such as tobacco use is also crucial for reducing the risk of gum disease.
1. Proper Care and Maintenance
Following a strict oral care routine can prevent the worsening of gum disease. This includes:
- Brushing twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque
- Flossing daily to clean between the teeth
- Using an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen bad breath
- Regular visits to the dental hygienist for professional cleaning
2. Healthy Diet
Incorporating a healthy diet rich in green leafy vegetables and dairy products can support healthy teeth and bones. Avoiding sugary and acidic foods will also protect the tooth enamel from erosion.
3. Home Remedies

Certain home remedies may offer relief from the symptoms of gum disease. For example, a saltwater gargle can help reduce inflammation and fight bacteria. Black pepper mixed with salt can also be applied to the gums to promote healing.
4. Mouth Guards
For patients who grind their teeth at night (bruxism), a mouth guard may be prescribed. This helps to protect the teeth from excessive wear and tear, preventing further loosening.
The Role of the Dental Professional
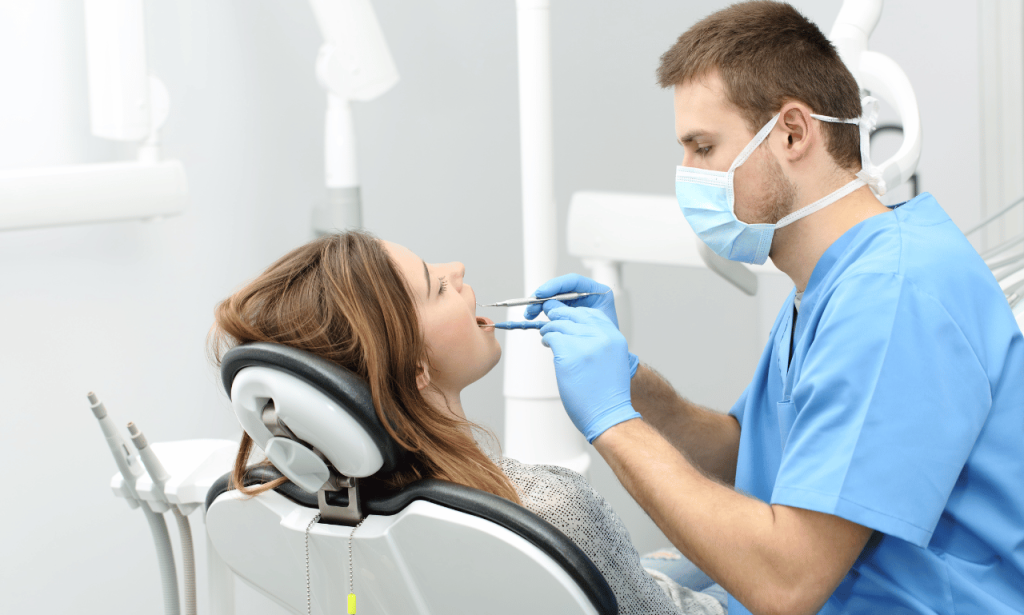
A dental professional will assess the severity of gum disease and create a treatment plan that addresses the underlying cause of your loose teeth. This may involve x-rays, a dental probe, or a detailed examination of the affected area. In some cases, underlying medical conditions like heart disease, high blood pressure, or pregnant women experiencing hormonal changes may affect the course of treatment.
1. Dental X-rays
To determine the extent of bone loss and gum disease, the dentist may take dental x-rays. This imaging will show whether the bone supporting the teeth is deteriorating and whether any dental surgery is required.
2. Early Stages of Gum Disease Treatment
Treating gum disease in its early stages can prevent tooth loss and the need for invasive procedures. Early intervention, such as deep cleaning or root planing, can stop the progression of the disease and secure loose teeth before they become a dental emergency.
3. Hormonal Changes
In some cases, hormonal changes can contribute to gum disease, especially in women. Pregnant women, in particular, may experience gum inflammation or even premature births due to oral infections. Understanding these connections allows for tailored treatment options.
The Connection Between Gum Disease and Systemic Health
Research has shown that gum disease is linked to various health conditions, including heart disease, high blood pressure, and a weakened immune system. This highlights the importance of oral health in maintaining overall wellness.
1. Health Conditions Related to Gum Disease
Chronic gum disease may increase the risk of other oral diseases, such as tooth decay and infection of the gums. The immune system plays a crucial role in fighting off these infections, but when compromised, it can lead to a faster progression of the disease.
2. Treatment for Patients with Medical Conditions
For patients with underlying medical conditions, special care is needed. Managing high blood pressure or heart disease alongside gum disease may involve working with both a dentist and a medical doctor to ensure that treatments do not conflict.
Final Thoughts: The Best Way Forward for Loose Teeth
Fixing loose teeth due to gum disease requires a combination of professional dental treatment, proper care at home, and an understanding of the underlying cause of the problem. Early detection is key, and the best option is to address gum disease before it advances to the point of severe bone damage.
The good news is that with advancements in dental technology, even severe cases of gum disease can be treated effectively. Whether you need root planing, bone grafting, or dental implants, there are options available to restore your dental health.
By following a comprehensive treatment plan, staying diligent with good oral hygiene habits, and seeking the help of a dental professional, you can prevent further damage and enjoy healthy gums and teeth for years to come.
For more personalized advice and the latest gum disease treatment options in 2025, click here to get started on your journey to better gum health.
Question and Answer
Bone Graft
Q: What is a bone graft, and when is it used?
A: A bone graft is a surgical procedure that uses bone material to repair and rebuild damaged bone in the jaw, often due to advanced gum disease. It’s commonly used when bone loss has occurred due to periodontal disease, trauma, or missing permanent teeth.
Bacterial Infection
Q: How does a bacterial infection impact dental health?
A: A bacterial infection in the gums leads to inflammation of the gums (gingivitis or periodontitis), which can progress to advanced gum disease if untreated. This weakens the bone and tissues supporting the teeth.
Poor Dental Hygiene
Q: How does poor dental hygiene contribute to gum disease?
A: Poor dental hygiene, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, allows plaque to build up on teeth. This plaque leads to bacterial infection and inflammation, causing gum disease over time.
Permanent Teeth
Q: Can permanent teeth become loose?
A: Yes, loose adult teeth are often a sign of underlying gum disease or bone loss, which can compromise the stability of permanent teeth.
Advanced Gum Disease
Q: What is advanced gum disease?
A: Advanced gum disease, or periodontitis, is a severe stage of gum infection where the gums pull away from the teeth, and bone loss occurs, potentially leading to tooth loss if not treated promptly.
Inflammation of the Gums
Q: What causes inflammation of the gums?
A: Inflammation of the gums is usually caused by bacterial infection due to plaque buildup from poor dental hygiene. It can lead to painful gums and eventually tooth loss.
Appropriate Treatment
Q: What is the appropriate treatment for advanced gum disease?
A: Appropriate treatment includes deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), bone grafts, flap surgery, or dental implants, depending on the extent of damage.
Painful Gums
Q: What can cause painful gums?
A: Painful gums are often a result of inflammation, infections, or injury, which may stem from gum disease, trauma, or irritants like poor-fitting dental appliances.
Dental Bridge
Q: What is a dental bridge?
A: A dental bridge is a prosthetic device used to replace one or more missing teeth by anchoring to adjacent teeth. It helps restore functionality after tooth loss due to gum disease or other dental issues.
Main Reasons
Q: What are the main reasons for loose teeth in adults?A:
The main reasons for loose adult teeth include advanced gum disease, trauma, bruxism (teeth grinding), and systemic health issues that affect bone and gum health.
Hydrogen Peroxide
Q: Can hydrogen peroxide be used for gum disease?
A: Hydrogen peroxide can be used as a mouth rinse to kill bacteria and reduce inflammation. It is a common home remedy to help manage early signs of gum disease.
Loose Adult Teeth
Q: Can loose adult teeth be saved?
A: Loose adult teeth can sometimes be saved with the right intervention, such as deep cleaning, bone grafting, or bite adjustments, depending on the severity of the condition.
Loose Adult Tooth
Q: What should you do if you have a loose adult tooth?
A: If you have a loose adult tooth, see a dentist immediately to determine the cause and receive proper treatment. Early intervention can prevent further damage.
Dental Clinic
Q: Why is visiting a dental clinic important for gum disease?
A: Visiting a dental clinic is crucial for diagnosing and treating gum disease early. Professional cleaning and appropriate treatments can prevent complications such as tooth loss.
Dental Issues
Q: What common dental issues are linked to gum disease?
A: Common dental issues related to gum disease include loose teeth, gum recession, bone loss, and infections, all of which can lead to tooth loss if untreated.
Risk Factor
Q: What are the risk factors for gum disease?
A: Risk factors for gum disease include poor dental hygiene, smoking, diabetes, genetic factors, hormonal changes, and certain medications that affect the gums.
Health Issues
Q: How can gum disease lead to other health issues?
A: Gum disease has been linked to systemic health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, as chronic inflammation in the gums can spread harmful bacteria throughout the body.
Salt Water
Q: Is salt water effective for gum disease?
A: Salt water rinses can help reduce swelling, clean out infections, and promote healing in the gums. It’s a useful home remedy for managing early symptoms of gum disease.