Gout is a painful form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. This condition can lead to intense pain, especially in the big toe, and is often triggered by dietary choices. Managing gout involves understanding which foods to avoid and which ones can be safely included in your diet.
This article will explore whether corn is safe to eat for gout sufferers and provide comprehensive insights into other foods to avoid and beneficial dietary changes.
Understanding Gout and Uric Acid
Gout is characterized by high levels of uric acid in the blood, which can crystallize and deposit in the joints, causing inflammation and pain. Uric acid is a chemical compound formed from the breakdown of purines, which are found in certain foods and beverages. When the body produces too much uric acid or fails to excrete enough through the kidneys, gout symptoms can occur.
Symptoms of Gout
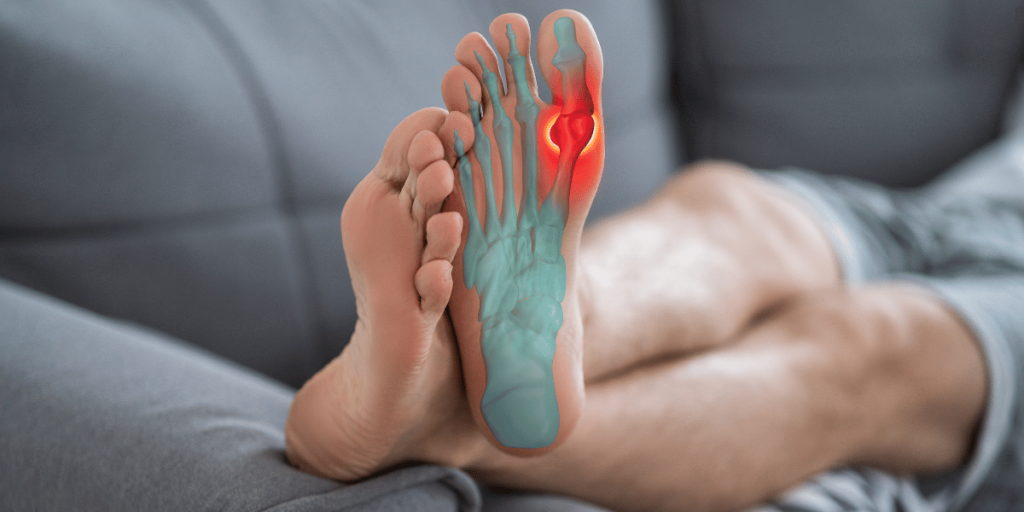
Common symptoms of gout include:
- Intense pain in the affected joint, often the big toe
- Swelling and redness around the joint
- Warmth and tenderness in the affected area
- Limited range of motion in the affected joint
Risk Factors and Health Conditions
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing gout, including:
- High levels of purines in the diet
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Cardiovascular disease
- Obesity
- Family history of gout
- Alcohol consumption
Corn and Gout: Is It Safe?

Corn is a staple food item in many diets around the world. It is relatively low in purines, making it a good option for those managing gout. Unlike red meat and organ meats, which are high-purine foods and can increase the risk of gout flares, corn does not significantly contribute to uric acid production. Including corn as part of a balanced diet can be beneficial for gout sufferers.
Benefits of Corn for Gout Sufferers
- Low in Purines: Corn has a low purine content, reducing the risk of increasing uric acid levels.
- Rich in Fiber: Corn is a whole grain and provides dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and can help maintain a healthy weight.
- Nutrient-Rich: Corn contains essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, which can help lower uric acid levels.
Foods to Avoid with Gout
To manage gout effectively, it’s crucial to limit the intake of high-purine foods and those that can trigger gout flare-ups. Here are some of the key foods to avoid:
1. Red Meat and Organ Meats
Red meats like beef, lamb, and pork, as well as organ meats such as liver and kidneys, are high in purines. These foods can significantly increase the level of uric acid in the blood, leading to gout attacks.
2. High-Fructose Corn Syrup
High-fructose corn syrup is commonly found in sugary drinks, soft drinks, and processed foods. It can increase uric acid production and is linked to a higher risk of gout attacks. Avoiding foods and beverages containing high-fructose corn syrup is a good idea for managing gout.
3. Alcoholic Beverages
Alcohol, especially beer and spirits, can raise uric acid levels and trigger gout flare-ups. Limiting alcohol consumption is essential for preventing future attacks and maintaining overall health.
4. Sugary Foods and Drinks
Sugary foods and drinks, including fruit juices and sweets, can contribute to high blood sugar levels and weight gain, both of which are risk factors for gout. Reducing the intake of sugary foods can help lower the risk of gout attacks.
5. High-Purine Vegetables
While most vegetables are beneficial, some have higher purine levels and should be consumed in moderation. These include asparagus, spinach, mushrooms, and cauliflower.
Dietary Changes for Managing Gout

Adopting a gout-friendly diet involves making dietary changes that can help lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout flare-ups. Here are some dietary approaches and foods to include:
1. Low-Purine Foods
Incorporating low-purine foods into your diet can help manage gout. These include:
- Whole grains (such as brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread)
- Low-fat dairy products (such as yogurt, milk, and cheese)
- Plant-based proteins (such as beans, lentils, and tofu)
- Healthy fats (such as olive oil, nuts, and avocados)
- Citrus fruits (such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits)
2. Drink Plenty of Water
Staying hydrated is crucial for gout sufferers. Drinking plenty of water helps the kidneys excrete uric acid more effectively, reducing its buildup in the body.
3. Tart Cherry Juice
Tart cherry juice has been shown to lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout attacks. Including tart cherry juice in your diet can be a beneficial addition for managing gout symptoms.
4. Regular Exercise
Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise can reduce the risk of gout attacks. Exercise helps improve overall health and can prevent the development of conditions such as high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, which are associated with gout.
5. Plant-Based Diet
Adopting a plant-based diet can be beneficial for gout sufferers. Plant-based foods are generally lower in purines and can help lower uric acid levels. Foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes should be the foundation of your diet.
6. Limit Animal Proteins
While animal proteins are a good source of nutrients, they can also be high in purines. Limiting the intake of animal proteins, such as red meat, poultry, and seafood, can help manage gout.
7. Avoid Yeast Extract
Yeast extract, commonly found in certain spreads and savory snacks, is high in purines. Avoiding foods with yeast extract can help reduce uric acid levels.
8. Balanced Diet
Following a balanced diet that includes a variety of low-purine foods, healthy fats, and whole grains can help manage gout effectively. Dietary changes should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider to ensure they meet your nutritional needs.
9. Mediterranean Diet and DASH Diet
Both the Mediterranean diet and the DASH diet are excellent options for gout sufferers. These diets emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins, which can help lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
Foods to Include in a Gout-Friendly Diet
Here are some specific food choices that can be included in a gout-friendly diet:
1. Low-Fat Dairy Products
Low-fat dairy products are low in purines and can help lower uric acid levels. Include yogurt, milk, and cheese in your diet for a good source of protein and calcium.
2. Whole Grains
Whole grains, such as brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread, provide essential nutrients and fiber. They are a healthier option compared to refined grains like white bread and white rice.
3. Citrus Fruits
Citrus fruits, such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits, are rich in vitamin C, which can help lower uric acid levels. Including these fruits in your diet can be beneficial for managing gout.
4. Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins, such as beans, lentils, and tofu, are low in purines and provide essential nutrients. They are a good alternative to animal proteins for gout sufferers.
5. Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and avocados, are beneficial for overall health and can help reduce inflammation associated with gout.
6. Tart Cherry Juice
Tart cherry juice has anti-inflammatory properties and can help lower uric acid levels. Including it in your diet can be a helpful addition for managing gout symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Gout
In addition to dietary changes, certain lifestyle changes can help manage gout effectively:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of gout attacks. Weight loss can help lower uric acid levels and reduce the burden on the joints.
2. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular exercise can improve overall health and help manage gout. Exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce inflammation, and improve kidney function.
3. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Limiting alcohol consumption, especially beer and spirits, can help reduce uric acid levels and prevent gout flare-ups. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for managing gout. Staying hydrated helps the kidneys excrete uric acid more effectively, reducing its buildup in the body.
5. Monitor Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a risk factor for gout. Monitoring and managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication can help reduce the risk of gout attacks.
6. Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor uric acid levels and manage gout effectively. Your healthcare provider can provide personalized dietary and lifestyle recommendations.
You want your gout cured, not managed. Right? But now there is a new discovery that changes everything about how we treat gout. End your gout HERE!
Conclusion
Managing gout involves making informed dietary choices and lifestyle changes to lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout flare-ups. Corn is a low-purine food that can be safely included in a gout-friendly diet.
However, it’s essential to avoid high-purine foods like red meat, organ meats, and sugary drinks containing high-fructose corn syrup. Incorporating low-purine foods, staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol consumption are crucial steps in managing gout.
Consulting with healthcare professionals and following a balanced diet, such as the Mediterranean or DASH diet, can provide comprehensive support for gout sufferers. By making these dietary and lifestyle
*Some of the links on this blog are affiliate links. This means if you click on the link and purchase the item, I will receive an affiliate commission.