What is the fastest way to recover from knee surgery, focusing on the roles of physical therapy, daily activities, medical advice, and lifestyle adjustments? We will discuss the importance of a strong healthcare team, managing pain, and the critical steps you can take to ensure the rehabilitation process is as smooth and efficient as possible.
Knee surgery is a significant procedure that can drastically improve mobility, reduce pain, and restore function, but recovery can take time and effort. Whether you’re undergoing total knee replacement (TKR), partial knee replacement, or another type of knee surgery, understanding how to accelerate the recovery process can be key to achieving the best outcomes.
Before diving into the specifics, a great resource to kickstart your recovery journey can be found here, which offers invaluable information and guidance for individuals recovering from knee surgery.
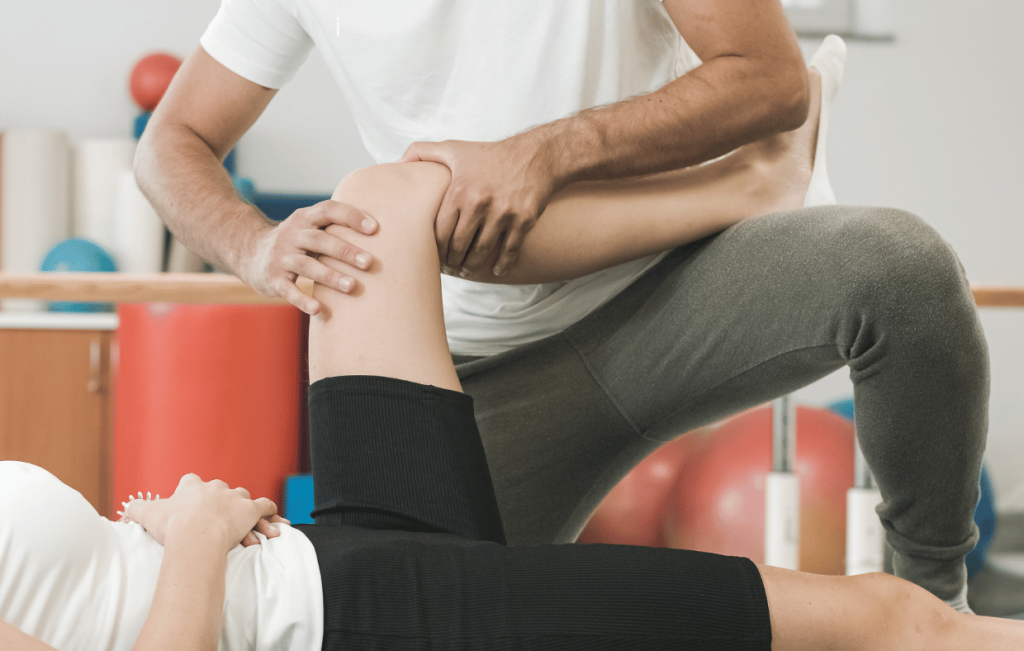

1. Understanding the Recovery Process
Knee surgery is typically performed to treat severe joint pain caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, trauma, or other knee joint issues. The recovery process varies depending on the type of surgery performed, but in general, the goal is to restore the knee joint’s function and improve mobility.
- Initial Phase of Recovery: The first few days after surgery are critical for managing pain and preventing complications such as blood clots. This phase typically involves resting the knee, using ice packs, and elevating the leg to reduce swelling. You will also be encouraged to begin gentle movements under the guidance of your healthcare team.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: After knee surgery, one of the most important factors for faster recovery is physical therapy. Physical therapists design a rehabilitation plan to strengthen the surrounding muscles, improve flexibility, and restore the range of motion (ROM). Regular physical therapy sessions are crucial for rebuilding strength and ensuring the knee joint works properly.
- Full Recovery Timeline: Recovery time varies, with a typical full recovery period taking anywhere from three to six months, and sometimes up to 18 months for more complex surgeries like total knee replacements. The speed of recovery will depend on factors such as your general health, the type of surgery, and how well you follow your rehabilitation plan.
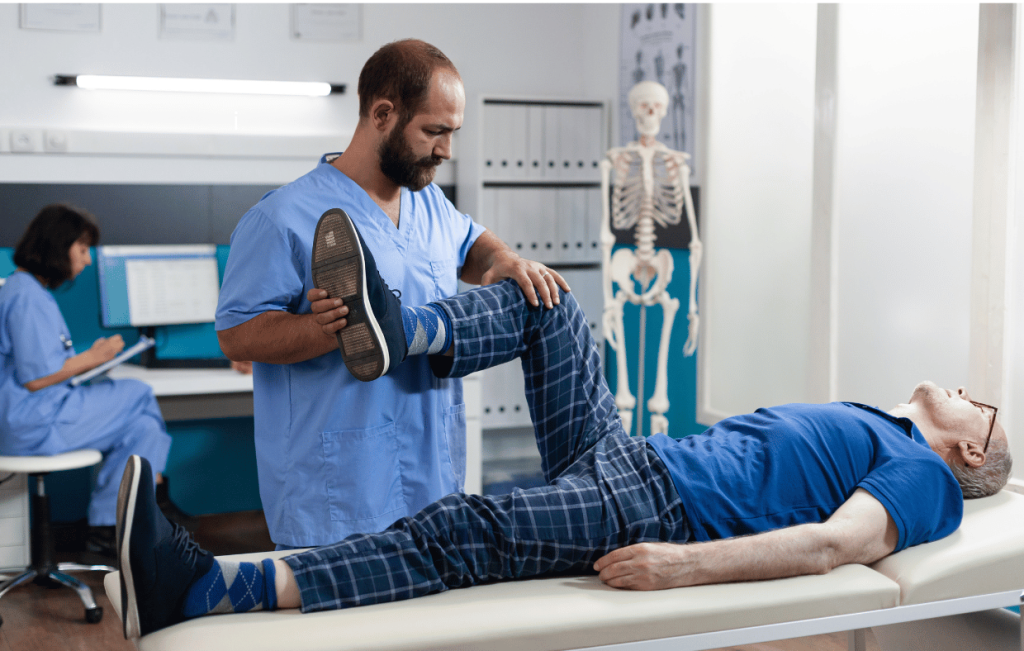
2. The Role of Physical Therapy in Accelerating Recovery
Physical therapy is essential for regaining function after knee surgery. After the initial healing process, typically within the first week, physical therapy will focus on:
- Improving Range of Motion: A key goal of physical therapy is to restore the knee’s range of motion. Without proper ROM, the knee may remain stiff, limiting your ability to perform everyday activities.
- Strengthening the Knee Joint: Strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee joint is essential for stabilizing the knee and improving mobility. Therapists will guide you through specific exercises to target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
- Preventing Scar Tissue Build-Up: Scar tissue can form as part of the healing process and may restrict movement. A physical therapist will incorporate stretching exercises to reduce the formation of excessive scar tissue and maintain joint flexibility.
- Reducing Pain: Physical therapy can help manage post-surgical pain through targeted exercises and modalities like ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation, and massage.

3. Managing Pain and Swelling
One of the most common challenges after knee surgery is managing pain and swelling. These symptoms can be minimized through:
- Pain Medication: Your healthcare provider may prescribe pain medication during the early stages of recovery. Opioids may be prescribed initially for severe pain, but they are typically phased out in favor of over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Ice Packs: Applying ice to the knee several times a day for 20 minutes at a time helps reduce swelling and provides pain relief. Ice therapy is particularly beneficial in the first few days after surgery.
- Knee Brace: If recommended by your surgeon, a knee brace can provide additional support and help keep the knee aligned as you begin moving around.
- Elevating the Leg: Elevating your leg above heart level can also assist in reducing swelling and promoting blood circulation, which aids in the healing process.
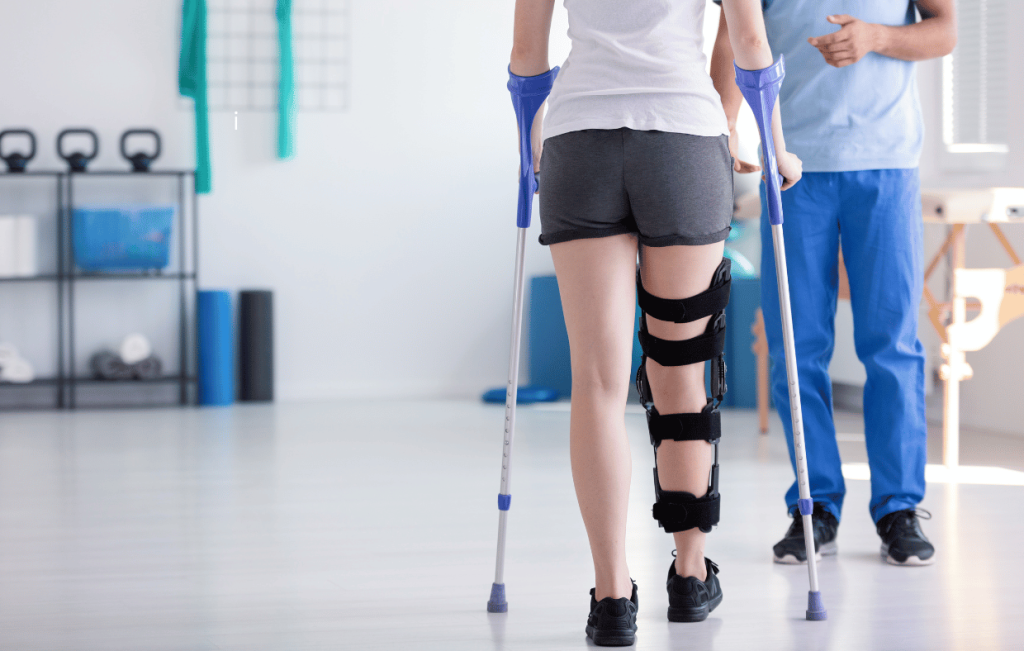

4. Mobility Aids and Assistive Devices
In the early stages of recovery, using mobility devices such as crutches, walkers, or walking sticks is common. These devices help reduce the weight on your healing knee, making it easier to move around while avoiding strain on the joint.
The type of mobility device used will depend on your activity level and the advice of your healthcare team. Some patients use these devices only for short walks or for assistance with balancing, while others may need them for longer distances.
- Walking Sticks and Walking Aids: Walking sticks or canes provide support and balance, especially if you experience instability or weakness in the knee. Your therapist will advise on when it’s appropriate to start reducing reliance on these aids.
- Shower Chairs and Grab Bars: These aids help ensure safety in the bathroom and prevent the risk of falling, especially during the initial recovery period when you may experience limited mobility.
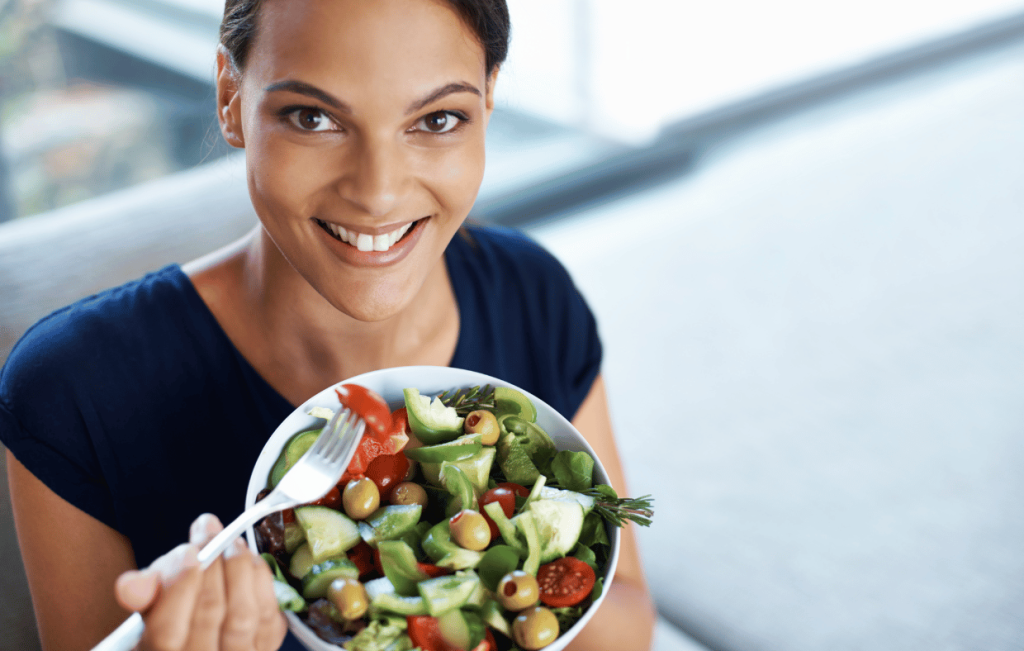

5. The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Nutrition plays a crucial role in the recovery process. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients will support healing, reduce inflammation, and provide the energy required for physical therapy and daily activities. Key nutrients include:
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair and tissue healing.
- Vitamins C and E: Important for reducing inflammation and promoting wound healing.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Vital for bone health, especially after joint surgery.
- Whole Grains: Provide sustained energy and promote overall health.
Additionally, staying hydrated is essential for the healing process, so drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day is highly recommended.

6. Gradually Increasing Activity Levels
Once your knee has begun healing and you’ve gained some strength through physical therapy, your activity level can gradually increase. It’s important to follow the guidance of your healthcare team and physical therapist when progressing to ensure that you don’t overexert yourself or risk further injury.
Here are some steps for gradually increasing activity:
- Short Walks: In the initial recovery period, you may begin by walking short distances. As your strength improves, you can gradually increase the distance and duration of your walks.
- Low-Impact Exercises: After the first few weeks, you can begin low-impact activities like swimming, stationary biking, or using an elliptical machine. These exercises are gentle on the knee while improving strength and cardiovascular health.
- Avoiding High-Impact Activities: High-impact activities like running, jumping, or playing contact sports should be avoided until your knee has regained sufficient strength and range of motion. Your physical therapist will advise you when it’s safe to return to these activities.
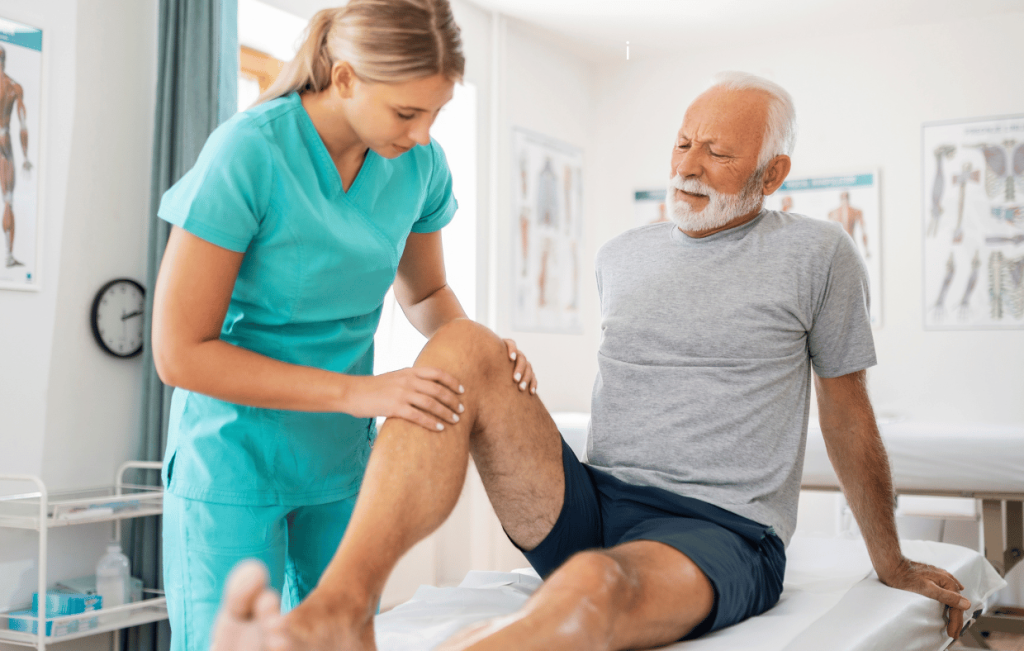
7. Follow-Up Appointments and Monitoring Progress
Regular follow-up appointments with your orthopedic surgeon and healthcare team are essential for monitoring your recovery. During these appointments, your surgeon will assess the healing of your knee joint, check for signs of infection, and make adjustments to your treatment plan as necessary.
- Surgical Site Monitoring: Your healthcare team will also monitor the surgical site for any signs of complications, such as infection or excessive swelling.
- Adjusting Treatment Plans: Based on your progress, your physical therapy plan and recovery goals may be adjusted. It’s important to communicate openly with your medical team about any concerns you have during this process.
8. Risk of Complications and How to Prevent Them
While most people recover from knee surgery without complications, there are risks that you should be aware of. The most common complications include:
- Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious concern after knee surgery. To reduce the risk of blood clots, it’s important to follow your surgeon’s recommendations regarding medications, compression stockings, and staying mobile.
- Infection: Proper care of the surgical site, including keeping it clean and dry, is essential for preventing infections. If you notice any unusual redness, warmth, or discharge, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
- Stiffness or Scar Tissue: If not properly managed, stiffness and scar tissue may impede your knee’s range of motion. Following your physical therapy plan and performing prescribed exercises can help reduce this risk.
Conclusion: A Successful and Faster Recovery
The fastest way to recover from knee surgery is a combination of careful planning, following medical advice, and staying active within the recommended limits. A well-rounded rehabilitation plan that includes physical therapy, proper pain management, a balanced diet, and appropriate use of mobility devices is essential.
The key to success is a proactive approach, staying patient, and continuously working towards your recovery goals. By following the advice of your healthcare team and gradually increasing your activity level, you can achieve a successful recovery and restore full function to your knee.